You are going to build a stone wall. The wall should be straight and N meters long, and its thickness should be constant; however, it should have different heights in different places. The height of the wall is specified by an array H of N positive integers. H[I] is the height of the wall from I to I+1 meters to the right of its left end. In particular, H[0] is the height of the wall's left end and H[N−1] is the height of the wall's right end.
The wall should be built of cuboid stone blocks (that is, all sides of such blocks are rectangular). Your task is to compute the minimum number of blocks needed to build the wall.
Write a function:
class Solution { public int solution(int[] H); }
that, given an array H of N positive integers specifying the height of the wall, returns the minimum number of blocks needed to build it.
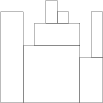
For example, given array H containing N = 9 integers:
H[0] = 8 H[1] = 8 H[2] = 5 H[3] = 7 H[4] = 9 H[5] = 8 H[6] = 7 H[7] = 4 H[8] = 8the function should return 7. The figure shows one possible arrangement of seven blocks.
Write an efficient algorithm for the following assumptions:
- N is an integer within the range [1..100,000];
- each element of array H is an integer within the range [1..1,000,000,000].
using System;
// you can also use other imports, for example:
using System.Collections.Generic;
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// Console.WriteLine("this is a debug message");
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] H)
{
int blocks = 0;
var levels = new Stack<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < H.Length; i++)
{
if (levels.Count == 0)
{
levels.Push(H[i]);
}
else
{
var lastLevel = levels.Peek();
if (lastLevel < H[i])
{
levels.Push(H[i]);
}
else if (lastLevel == H[i])
{
// nothing to do
}
else // lastLevel > H[i]
{
// keep popping levels until one is smaller than the current one
while (true)
{
levels.Pop(); // pop the last level
blocks++; // increment the block counter
if (levels.Count == 0)
{
// nothing left to pop
levels.Push(H[i]); // push current level
break;
}
// else, there are more levels in the stack
lastLevel = levels.Peek();
if (lastLevel < H[i])
{
// no need to pop-up any more levels
levels.Push(H[i]); // push current level
break;
}
else if (lastLevel == H[i])
{
// no need to pop-up any more levels and no need to push a new level either
break;
}
// else, repeat the while loop
}
}
}
}
blocks += levels.Count;
return blocks;
}
}using System;
// you can also use other imports, for example:
using System.Collections.Generic;
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// Console.WriteLine("this is a debug message");
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] H)
{
int blocks = 0;
var levels = new Stack<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < H.Length; i++)
{
if (levels.Count == 0)
{
levels.Push(H[i]);
}
else
{
var lastLevel = levels.Peek();
if (lastLevel < H[i])
{
levels.Push(H[i]);
}
else if (lastLevel == H[i])
{
// nothing to do
}
else // lastLevel > H[i]
{
// keep popping levels until one is smaller than the current one
while (true)
{
levels.Pop(); // pop the last level
blocks++; // increment the block counter
if (levels.Count == 0)
{
// nothing left to pop
levels.Push(H[i]); // push current level
break;
}
// else, there are more levels in the stack
lastLevel = levels.Peek();
if (lastLevel < H[i])
{
// no need to pop-up any more levels
levels.Push(H[i]); // push current level
break;
}
else if (lastLevel == H[i])
{
// no need to pop-up any more levels and no need to push a new level either
break;
}
// else, repeat the while loop
}
}
}
}
blocks += levels.Count;
return blocks;
}
}using System;
// you can also use other imports, for example:
using System.Collections.Generic;
// you can write to stdout for debugging purposes, e.g.
// Console.WriteLine("this is a debug message");
class Solution {
public int solution(int[] H)
{
int blocks = 0;
var levels = new Stack<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < H.Length; i++)
{
if (levels.Count == 0)
{
levels.Push(H[i]);
}
else
{
var lastLevel = levels.Peek();
if (lastLevel < H[i])
{
levels.Push(H[i]);
}
else if (lastLevel == H[i])
{
// nothing to do
}
else // lastLevel > H[i]
{
// keep popping levels until one is smaller than the current one
while (true)
{
levels.Pop(); // pop the last level
blocks++; // increment the block counter
if (levels.Count == 0)
{
// nothing left to pop
levels.Push(H[i]); // push current level
break;
}
// else, there are more levels in the stack
lastLevel = levels.Peek();
if (lastLevel < H[i])
{
// no need to pop-up any more levels
levels.Push(H[i]); // push current level
break;
}
else if (lastLevel == H[i])
{
// no need to pop-up any more levels and no need to push a new level either
break;
}
// else, repeat the while loop
}
}
}
}
blocks += levels.Count;
return blocks;
}
}The solution obtained perfect score.